🧬 What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
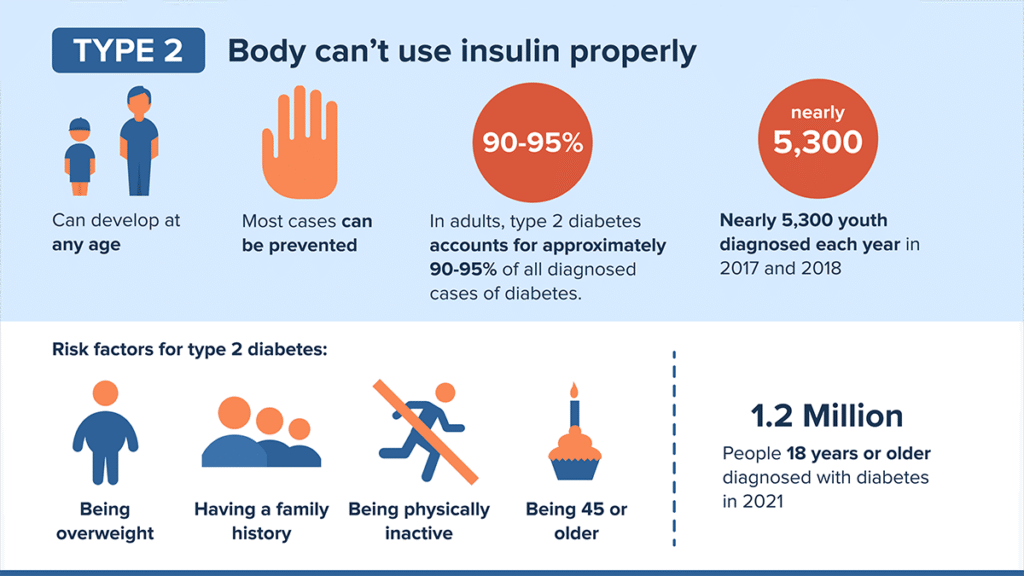
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels resulting from insulin resistance and progressive beta-cell dysfunction in the pancreas. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, which involves autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells, Type 2 diabetes is typically acquired and closely linked to lifestyle factors, chronic inflammation, and environmental influences.
Over time, cells in the liver, muscle, and fat become less responsive to insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. To compensate, the pancreas produces more insulin—leading to hyperinsulinemia, which itself becomes a driver of weight gain, fatigue, and vascular damage.
If left unaddressed, T2DM increases the risk of:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney failure (diabetic nephropathy)
- Retinal damage (diabetic retinopathy)
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Cognitive decline and dementia
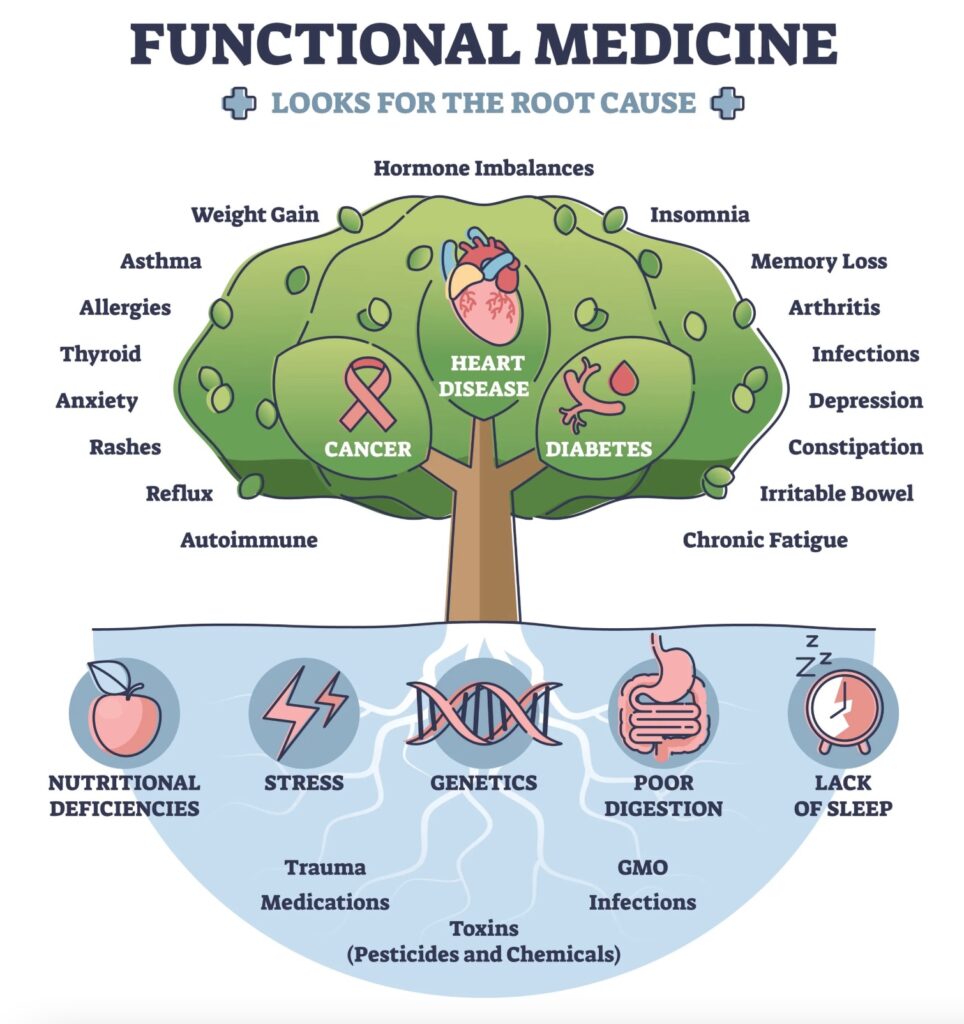
Conventional treatment often focuses on blood sugar control through medication, without addressing the upstream causes of insulin resistance. Functional medicine seeks to interrupt disease progression by correcting the imbalances that drive it.