Hormone Replacement Therapy is a treatment to replaces hormones that are at a lower level. We use hormone baseline test results to prescribe hormone replacement therapy to bring your patient’s hormones to their optimum targeted levels. Then, monitor hormone levels with periodic follow-up visits and re-testing to assess the effectiveness of the therapy and adjust as necessary.
What is Hormone Replacement Therapy?

Hormone Replacement Therapy For Women
Estrogen Replacement Therapy (ERT)
The principal estrogens in a woman are estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estradiol is the most potent of these estrogens and is produced by the ovary. Estrone and estriol are both metabolites of estradiol and are less potent, with estriol being the weakest.
Progesterone Replacement Therapy
Progesterone (P4) is a hormone produced in women by the adrenal glands, the ovaries and in the placenta during pregnancy. Progesterone interacts with and mediates estrogen. Progesterone is known as a precursor hormone for estrogen, luteinizing hormone, and testosterone, among others. To a certain extent, progesterone controls the production of these other hormones and can help balance any deficiencies or excesses of them in your body. In addition to helping relieve the symptoms of menopause and PMS, progesterone is known to enhance energy and sexual libido, and to heighten feelings of well-being.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
Testosterone, although a primary male hormone, also plays a role in women’s health. A decline in testosterone levels in women may accompany a decreased libido, irritability, weight gain, loss of lean muscle and osteoporosis. Testosterone contributes to higher energy levels and overall sense of well-being, increases lean body mass, and helps in building strong bones.
Hormone Replacement Therapy For Men
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
A decline in testosterone levels in men may be indicated by symptoms including loss of libido, erectile dysfunction, deterioration in ability to concentrate, poor muscle tone and strength, lack of endurance and mood swings. Testosterone contributes to higher energy levels and overall sense of well-being, increases lean body mass, and helps in building strong bones.
For people not producing high enough levels of testosterone, Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) may be appropriate. This therapy should be considered when hormone deficiency has been clinically proven through laboratory testing of blood serum or saliva.
Want To Transform Your Life?
SERVICES
CONDITIONS WE TREAT
Thyroid & Hormone Balance
Hypothyroid, Hyperthyroid, Hashimoto Thyroiditis, Menopause, Hormone Replacement, PMS, Adrenal Fatigue, Low Libido, Erectile Dysfunction, etc.
Digestive Health & Nutrition
IBS, Food Sensitivites & Allergies, Constipation, Diarrhea, Candida or Yeast Overgrowth, Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO), Bloating, Indigestion, GERD, Parasites, etc.
Autoimmune & Inflammation
Lyme Disease, Hashimoto Thyroiditis, Graves Disease, Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Sjogrens, Multiple Sclerosis, Crohns, Ulcerative Colitis, Type 1 Diabetes, Psoriasis, Environmental Illness (Mold/Mycotoxins), etc.
Allergy, Sensitivity, & Intolerance
Holistic & Conventional treatments of Allergies, Candida, Food Sensitivities, Environmental Sensitivities, etc.
Cardiovascular & Metabolic Health
High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol, Heart Disease, Diabetes, Stroke, TIA, Low Blood Pressure, POTs, etc.

Energy & Brain Health
Depression, Anxiety, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS), Weight Gain, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Dementia, Insomnia, etc.
WHAT WE DO

Uncover the Root cause
We dig deep to find the root cause of your symptoms with advanced lab testing and an in-depth lifestyle review.

Treat Collaboratively
We partner with you to create a personalized protocol with dietary, lifestyle, and supplement strategies and provide accountability and support every step of the way.

Transform Your Health
Our model is geared toward long-term results. We provide ongoing support and tools you can use for life to optimize your health and recover from setbacks.
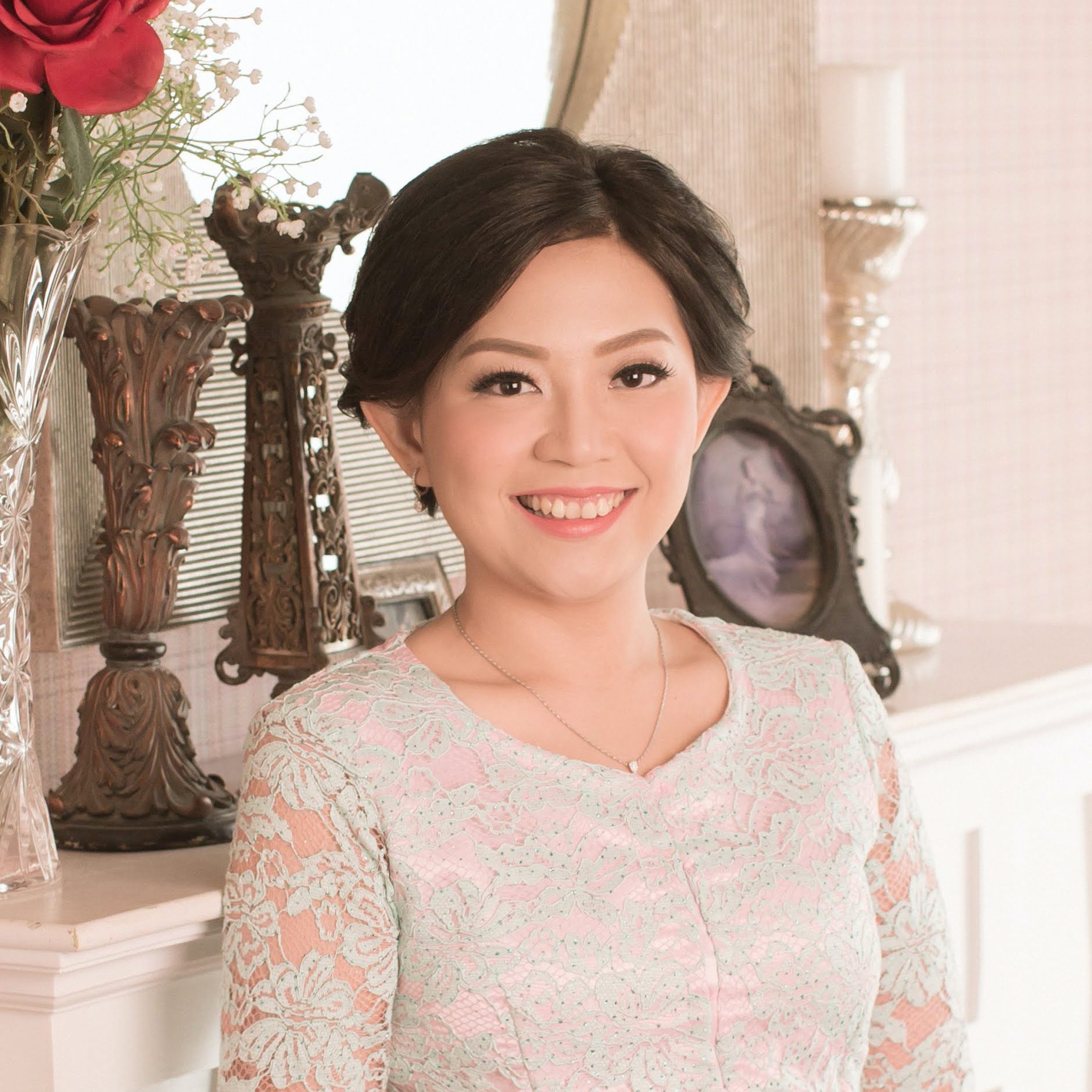

ABOUT DOCTOR
Hi, I’m Dr. dr. Linda Sinto, MARS, M.Biomed (AAM), FINEM, AIFO-K
Expert Anti Aging and Integrative Functional Medicine in Jakarta
Dr. dr. Linda Sinto is a passionate and experienced medical practitioner based in Indonesia. After graduating from medical school, she pursued a postgraduate program in Hospital Administration at Universitas Indonesia and continued her studies in Anti-Aging Medicine at Universitas Udayana. She later earned her doctoral degree from Universitas Udayana, further solidifying her expertise in the field.
Driven by her enthusiasm for optimizing health and wellness, Dr. Linda has participated in various advanced programs, including a DNA Diploma Certification, Fellowship in Nutritional and Environmental Medicine (FINEM), Fellowship in Anti-Aging, Metabolic, and Functional Medicine (FAAMFM), and Postgraduate Training in Evidence-Based Hormone Therapy at the Dr. Hertoghe Medical School.
CARE & EMPATHY
Because you are important, that’s why we would like to know you more as a whole person. We approach every patient as a unique individual with needs specific to your health.
CONSULTATION & TREATMENT
We offer professional consultations services to address the many and varied healthcare needs we all face every day. Evidence informed & guided medicine is the foundation of all our therapies. The aimed is to understanding your needs and guiding you to make educated decisions.